What is Production Management?
Production Planning and Scheduling
Effective production planning forms the foundation of successful operations. This involves forecasting demand, determining production capacity, scheduling resources, and creating detailed production timelines. Advanced planning systems help managers balance customer requirements with resource constraints while minimizing costs and maximizing throughput.
Quality Control and Assurance
Quality management ensures products meet specified standards and customer expectations. This includes implementing quality control checkpoints, statistical process control, continuous improvement programs, and comprehensive testing protocols. Modern quality systems integrate real-time monitoring and predictive analytics to prevent defects before they occur.
Inventory Management
Strategic inventory management balances the costs of holding stock with the need to meet customer demand. This involves optimizing raw material procurement, work-in-progress monitoring, and finished goods distribution. Advanced inventory systems use demand forecasting and automated replenishment to minimize carrying costs while preventing stockouts.
Resource Allocation and Capacity Planning
Efficient resource management ensures optimal utilization of equipment, personnel, and facilities. This includes workforce planning, equipment maintenance scheduling, and facility layout optimization. Capacity planning helps organizations prepare for future demand while maintaining operational flexibility.
Key Production Management Strategies
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste while maintaining quality and efficiency. Key principles include value stream mapping, continuous flow optimization, pull-based production systems, and employee empowerment. Organizations implementing lean methodologies typically see significant improvements in productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Production
JIT production minimizes inventory costs by producing goods only when needed. This approach requires strong supplier relationships, reliable demand forecasting, and flexible production systems. When properly implemented, JIT reduces waste, improves cash flow, and increases responsiveness to market changes.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM is a comprehensive approach that involves all employees in continuous quality improvement. This strategy emphasizes customer focus, employee involvement, process improvement, and data-driven decision-making. TQM creates a culture of quality that permeates every aspect of the organization.
Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing enables rapid response to changing market conditions through flexible production systems, cross-trained workforce, and modular equipment design. This approach helps organizations capitalize on opportunities while minimizing risks associated with market volatility.
Technology in Production Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Modern ERP systems integrate all aspects of production management into a unified platform. These systems provide real-time visibility into operations, automate routine tasks, and enable data-driven decision-making. Advanced ERP solutions include artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities for predictive analytics and automated optimization.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Manufacturing
IoT sensors and connected devices provide unprecedented visibility into production processes. Smart manufacturing systems collect and analyze real-time data to optimize performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve quality control. This technology enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending equipment life.
Automation and Robotics
Automated systems and robotics improve consistency, speed, and safety in production environments. From simple pick-and-place operations to complex assembly processes, automation technologies help organizations achieve higher productivity while reducing labor costs and improving working conditions.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Advanced analytics tools transform production data into actionable insights. These systems identify trends, predict problems, and recommend optimizations. Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns that human operators might miss, leading to continuous improvement opportunities.
Performance Metrics and KPIs
Operational Efficiency Metrics
Key performance indicators help managers monitor and improve production performance. Important metrics include overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), throughput rates, cycle times, and resource utilization. These measurements provide objective data for decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives.
Quality Metrics
Quality performance indicators include defect rates, first-pass yield, customer satisfaction scores, and cost of quality. Tracking these metrics helps organizations maintain high standards while identifying opportunities for improvement.
Financial Performance
Production management directly impacts financial performance through cost control, efficiency improvements, and quality enhancements. Key financial metrics include production costs per unit, return on assets, and contribution margins.
Best Practices for Production Management
Continuous Improvement Culture
Successful production management requires a commitment to continuous improvement. This involves regular process reviews, employee feedback programs, and systematic problem-solving methodologies. Organizations that embrace continuous improvement typically outperform their competitors in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective production management requires close collaboration between departments including engineering, quality, maintenance, and supply chain. Breaking down silos and promoting communication leads to better decision-making and improved overall performance.
Employee Training and Development
Investing in employee skills and knowledge pays dividends in improved performance and job satisfaction. Comprehensive training programs ensure workers understand their roles, safety procedures, and quality requirements. Ongoing development keeps skills current with evolving technologies and methodologies.
Supplier Relationship Management
Strong supplier partnerships are essential for production success. This includes supplier evaluation and selection, performance monitoring, and collaborative improvement initiatives. Effective supplier relationships ensure reliable material supply while driving cost reductions and quality improvements.
Future Trends in Production Management
Digital Transformation
The integration of digital technologies is revolutionizing production management. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics are creating new possibilities for optimization and control. Organizations that embrace digital transformation gain competitive advantages through improved efficiency and responsiveness.
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in production management. Sustainable practices include waste reduction, energy efficiency, and circular economy principles. Companies that prioritize sustainability often find cost savings while meeting stakeholder expectations.
Customization and Mass Personalization
Customer demand for customized products is driving changes in production management. Flexible manufacturing systems and digital technologies enable mass customization while maintaining efficiency. This trend requires new approaches to planning, scheduling, and quality control.
Conclusion
Production management is a critical discipline that directly impacts organizational success. By implementing proven strategies, leveraging advanced technologies, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can achieve operational excellence while meeting evolving customer demands. The future of production management lies in embracing digital transformation while maintaining focus on fundamental principles of efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Success in production management requires a holistic approach that considers all aspects of operations, from strategic planning to daily execution. Organizations that master these principles position themselves for sustained competitive advantage in an increasingly complex and dynamic business environment.
Production Management
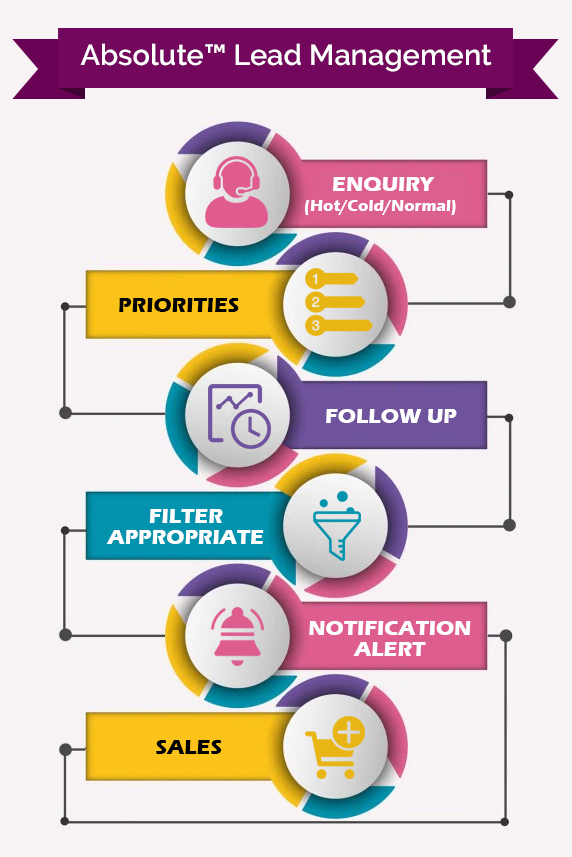
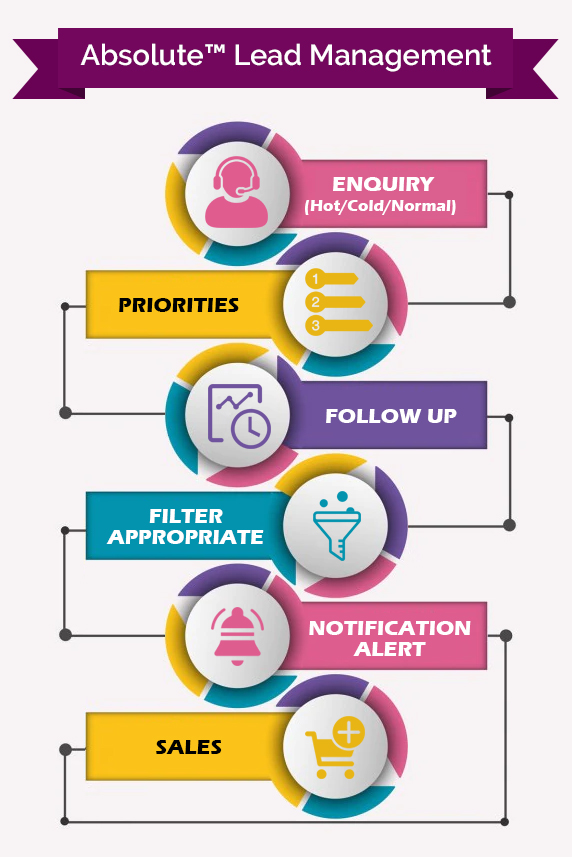
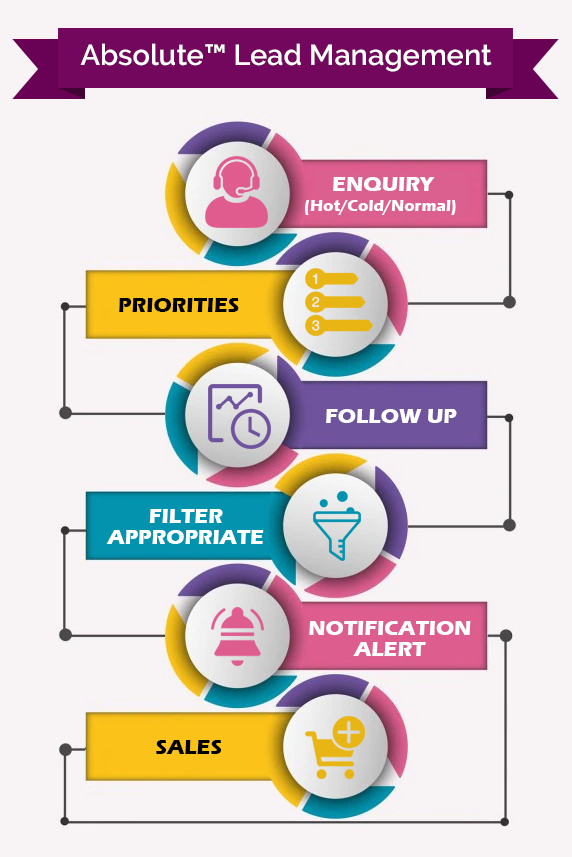
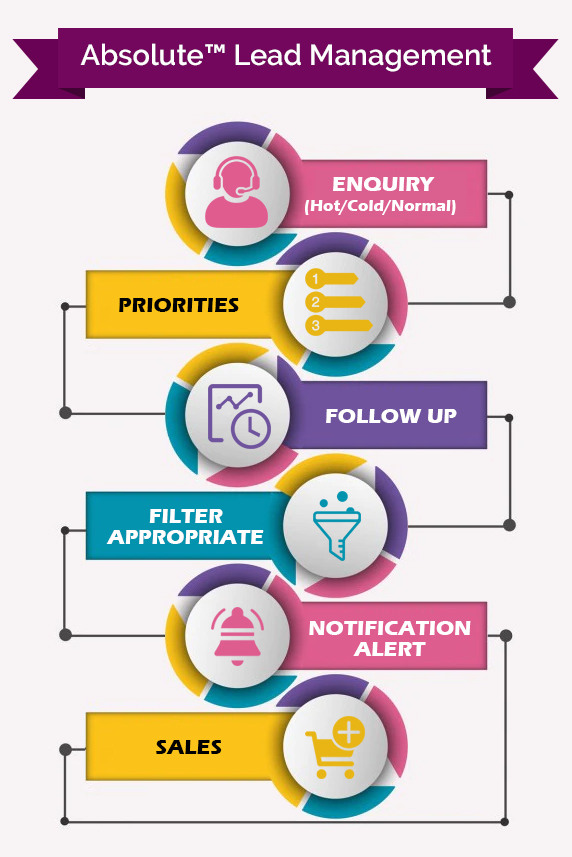
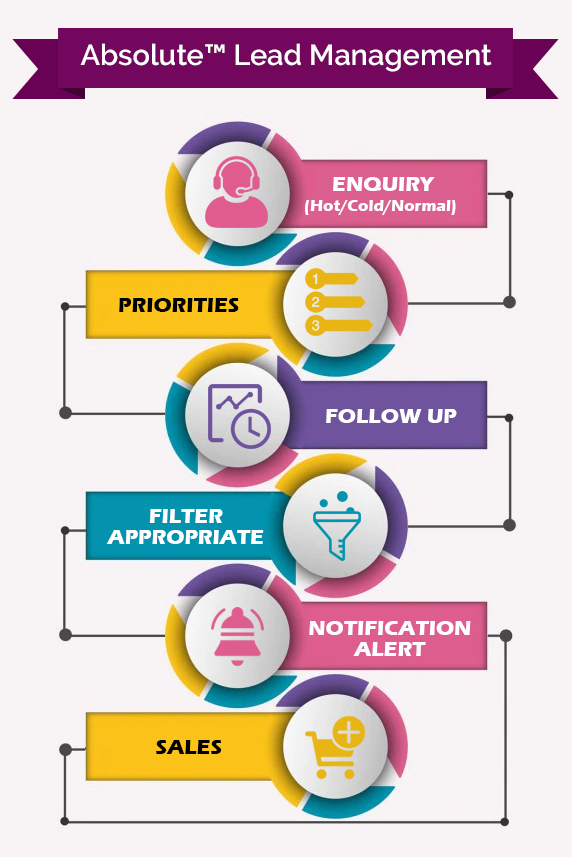
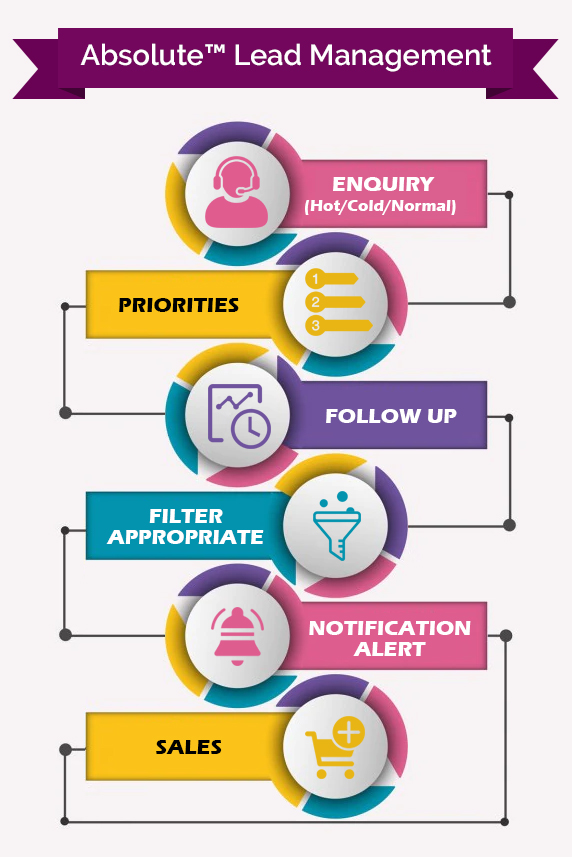
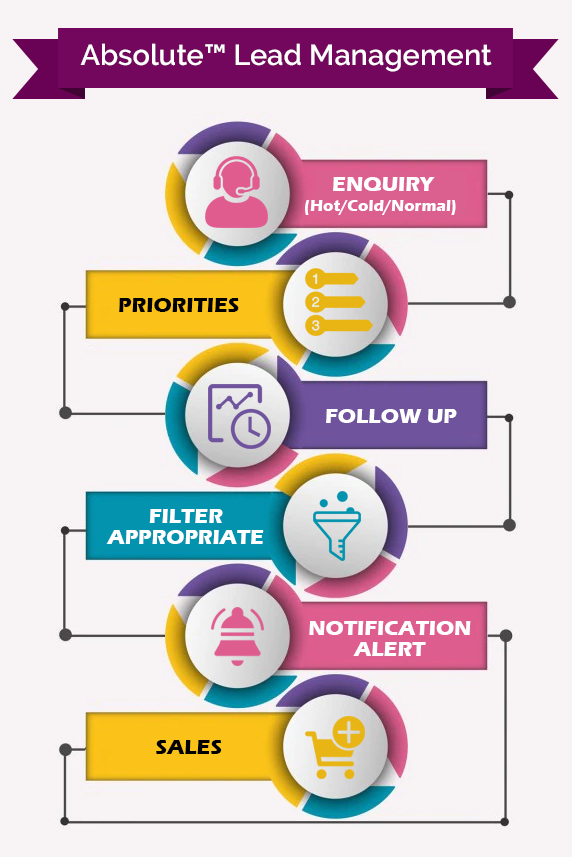
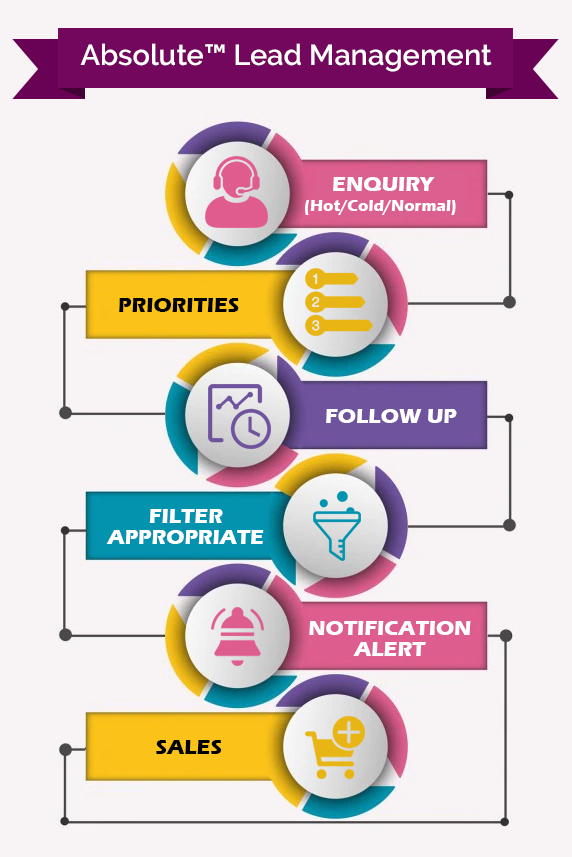
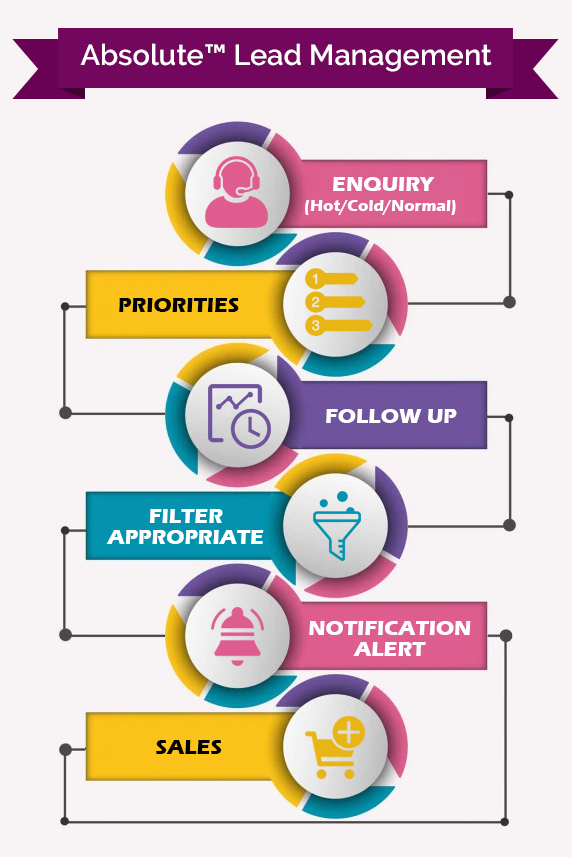
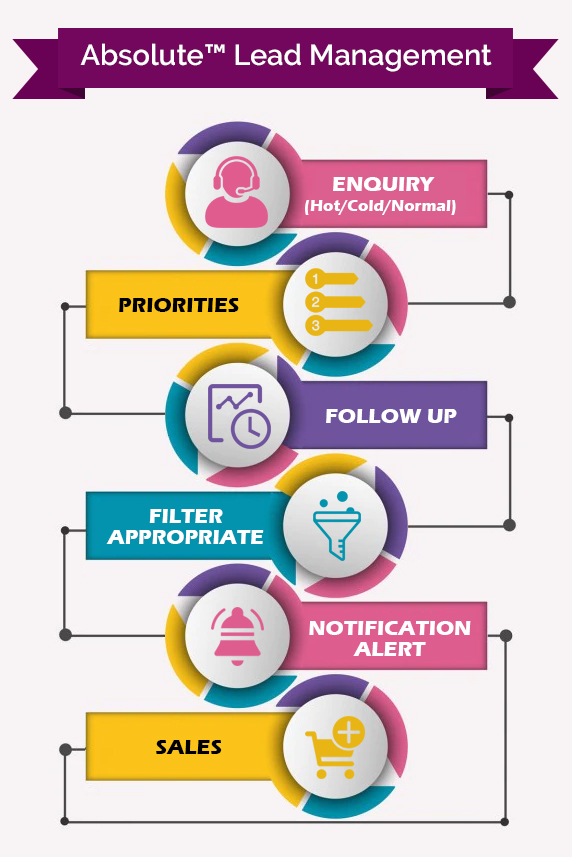
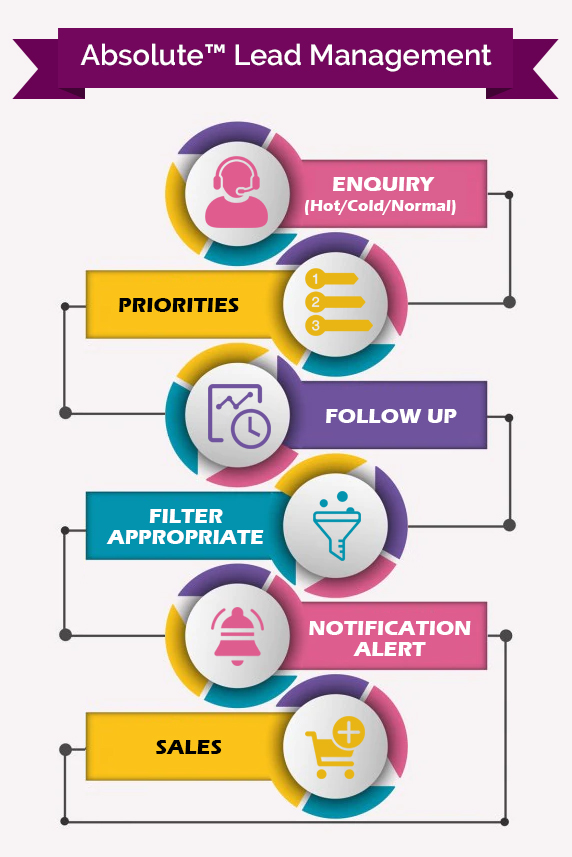
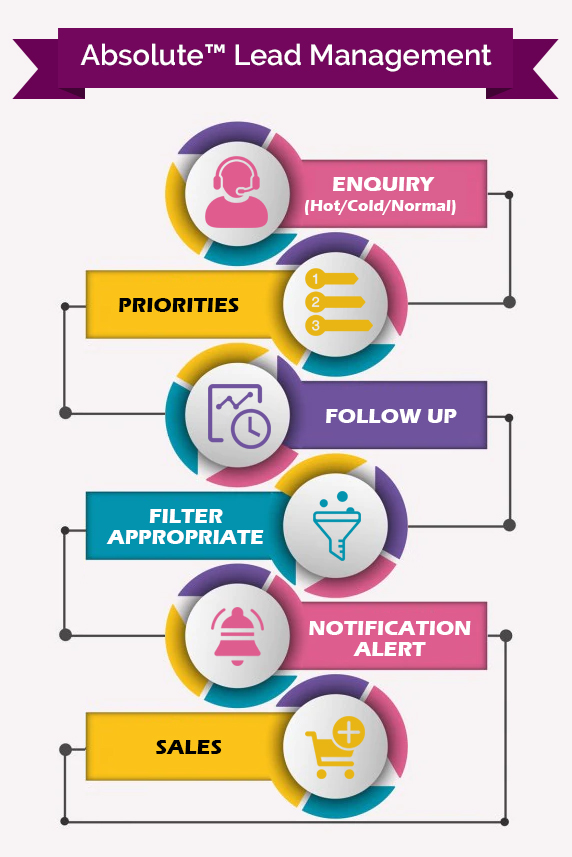
A Glimpse of Lead A Glimpse of Lead Management Software

Cloud Based Solution
Efficiently scalable, easily manageable, undeniably powerful

User Friendly Interface
User-Friendly interface offers a perfect work environment
Unlimited Users
Unlimited users account gives access to any information

Device Responsive
Get the Absolute ERP access on any device
Unlimited Storage
Expend your business with unlimited storage

Multi Language
Let Absolute ERP speaks your business language

Multi Currency
Get the best business deal with a multi-currency option

Detail MIS & Reports
Informative MIS reports for presentations